Insight:
- Coconut water forms through a fascinating process involving photosynthesis, xylem transport, and nutrient accumulation. It’s not just rainwater but a nutritious liquid rich in electrolytes and minerals.
- Despite myths about its origin, coconut water offers hydration, potential health benefits, and is a low-calorie alternative to sugary drinks.

You might have heard or been familiar with coconut water, but can you explain how coconuts get water in them? This article helps you discover the fascinating process of coconut water formation and how it helps your body function more effectively. Scroll down for further details!
What is coconut palm and its fruit?
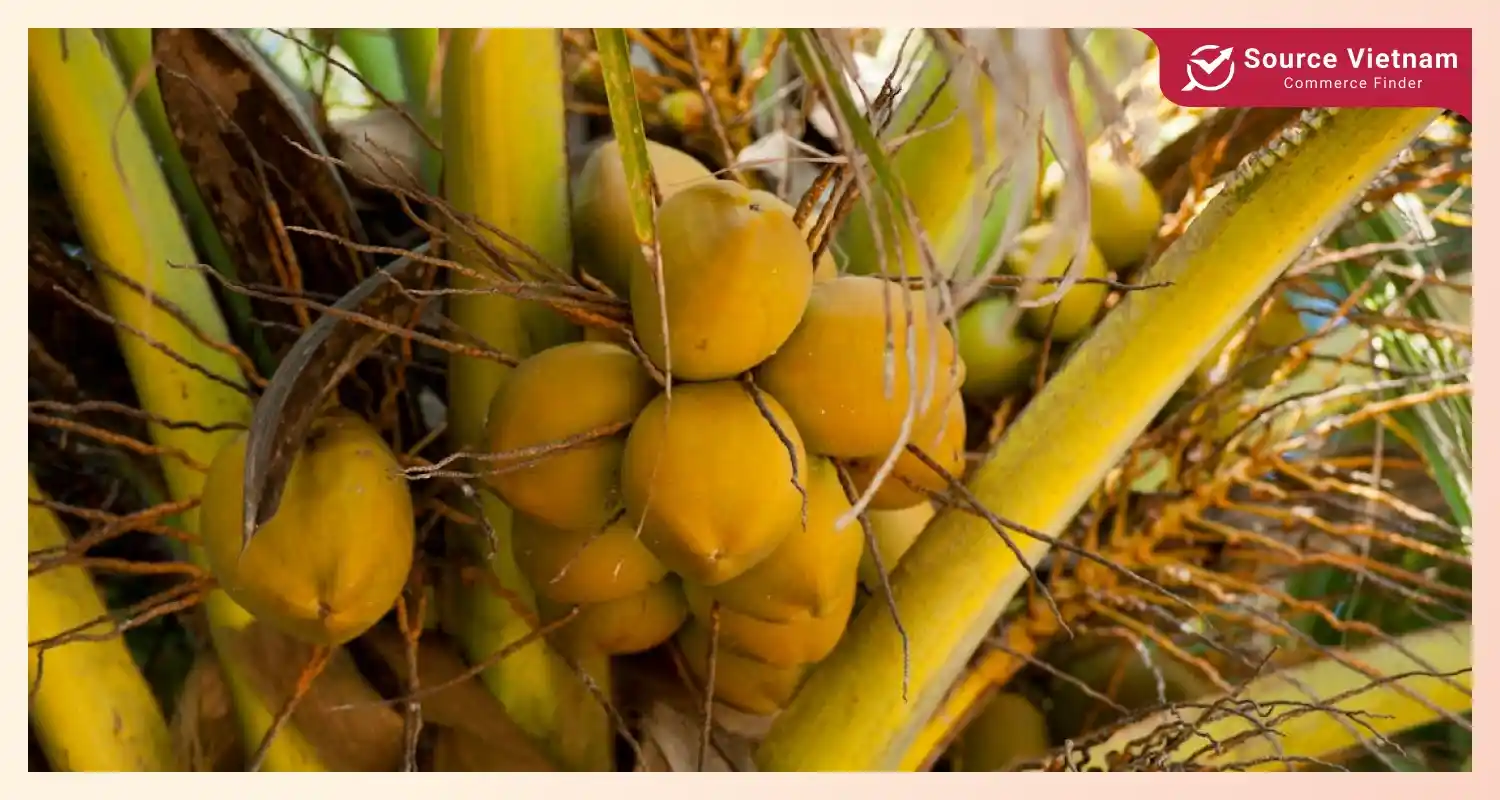
A coconut palm, also known as a coconut nucifera or simply as a coconut tree, is popular with versatile fruits in many tropical areas, such as Thailand, Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, etc. There will be coconut fruits yearly, making even 200 coconuts per tree. A coconut palm tree can produce its fruit in 80 years, which means you can enjoy its water for nearly a century.

Coconut water is one of the most beloved drinks in tropical countries. For those who are not familiar with this beverage type, it is contained in a coconut nut with three different layers, such as exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
“How does water get in coconuts?” you might be wondering. The following section will uncover how to explore the role of xylem vessels in transporting water within coconut trees.
Photosynthesis’s role in coconut water formation
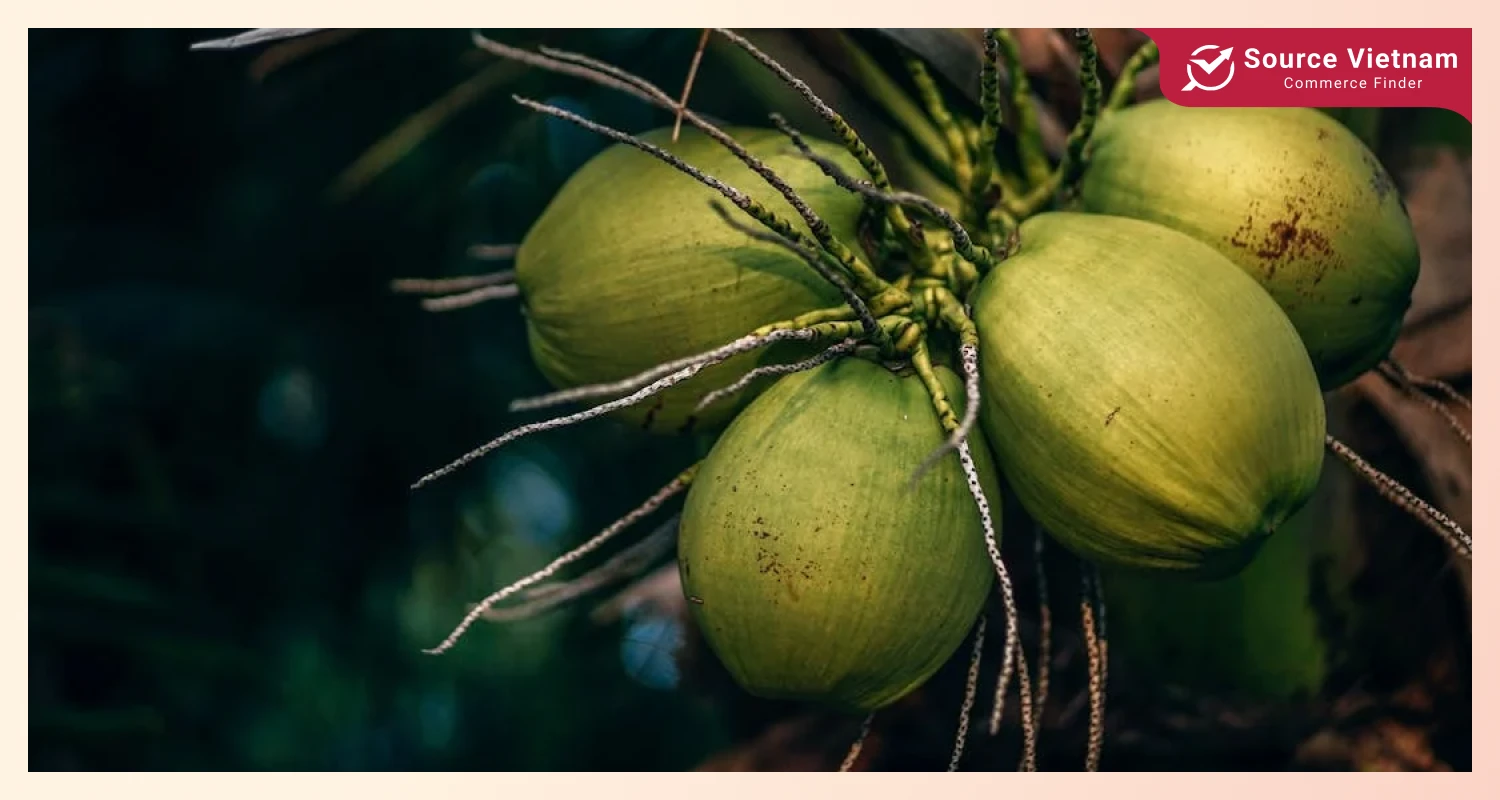
How do coconuts produce water inside? It sounds like a simple question, yet it opens up many interesting facts about the coconut water formation process, one of which is photosynthesis.
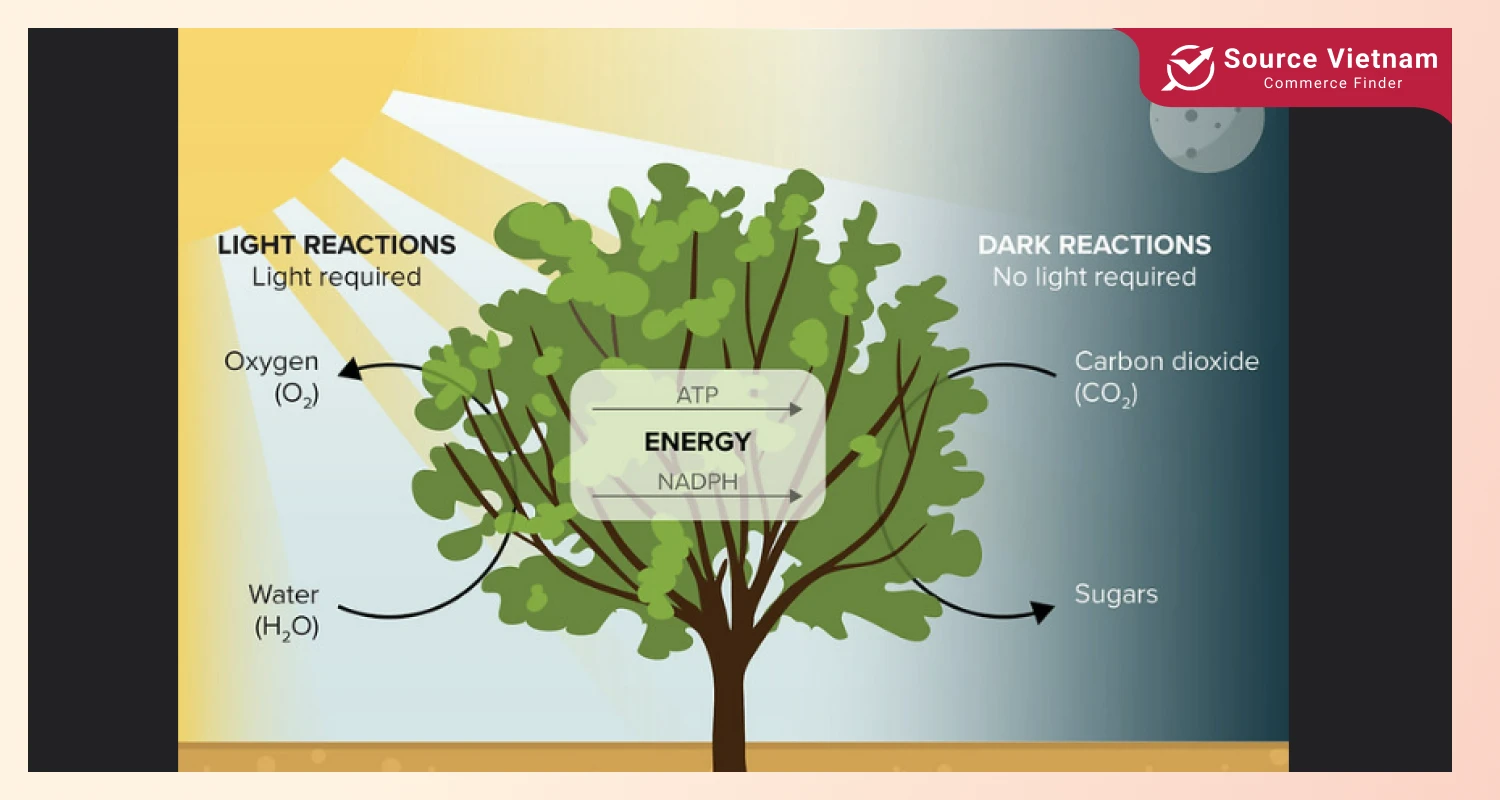
Photosynthesis refers to a process by which coconut trees transform sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into energy in the form of sugar and simultaneously create oxygen. Consequently, coconut roots absorb and transport water and minerals from the soil to every part of the tree, especially its fruit.
Plant water transport means-of are xylem vessels that form a complex network to enable efficient water delivery to coconut fruits. As the fruits mature, the endosperm will eventually become coconut meat and water, accumulating nutrients and water.
The brief walkthrough helps you learn how photosynthesis contributes to water accumulation in coconuts. Let’s dive deeper into coconut water production to enrich your knowledge about this simple yet healthy drink.
Read more >>> Top 10 Coconut Water Suppliers in Vietnam for 2025
How do coconuts get water in them?

How do coconuts get water inside? The question uncovers a complex process with many biochemical and physiological factors. A deep dive into this process can help you see how magical nature works and reward us with a tasty and healthy tropical drink of coconut.
Early stages
The coconut water formation in young coconuts generates a liquid endosperm. This liquid contains essential sugars, proteins, vitamins, and minerals to nourish the developing embryo and grow young coconuts. The endosperm will gradually develop into two separate layers, the outer and inner layers.
The outer layer forms a fibrous husk surrounding the coconut, while the inner layer differs into the white, fleshy coconut meat. Water in young and green coconuts has a refreshing taste with many health benefits.
Nutrient-rich liquid
The tree might lose a significant amount of water due to transpiration. Thus, coconut water production in coconuts relies on endosperm nutrients to build up the coconut water and differentiate layers inside the fruit.
Specifically, endosperm includes carbohydrates that energize the developing embryo while boosting the metabolic processes. Another nutrient is amino acids, which help coconuts develop the synthesis of new tissues and enzymes.
Besides, coconut development does not lack vitamins and minerals like potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, and vitamins B and C. Without these substances, coconut physiology processes might not work to their fullest.
Maturation process
Coconuts’ maturation time varies based on climate and specific coconut variety, yet it typically takes 11 to 12 months. During this process, a coconut goes through a remarkable transformation in terms of appearance and coconut water amount.
When a coconut matures, the lipid and protein content will increase. Hence, the endosperm becomes denser and more solid. Simultaneously, the cellular structure of the endosperm expands and accumulates storage products, including starch and oil.
As time passes and the endosperm is solidified, coconut water production will slow down. The liquid becomes the source of nutrients and water to thicken coconut meat.
Hopefully, The information helps you understand coconut water’s ecological significance in seed development. Although being popular among locals and foreign visitors, coconut water still has some misconceptions, which the next section illuminates.
Read more >>> Coconut Milk vs Coconut Water: Differences and Benefits
Common myths about coconut water

There are many misconceptions about coconut water, which we will debunk and bring out some interesting facts.
- Myth 1 – Coconut water is simply rainwater
Many people consider coconut water just rainwater accumulating inside the coconut through time. It is not wrong as coconut roots take water from the ground and transport it to the nut.
However, this process involves various factors and a sophisticated biological system to transform water from the roots into coconut water. So, ‘no’ is the response to the statement above, as coconut water is a complex fluid containing various nutrients and electrolytes.
- Myth 2 – Coconut produces seawater
As coconut palms are usually found near oceans, another common misconception is that coconut water is what the tree seeped from the sea. Yet, the water inside the coconut has a different taste and content from seawater. As mentioned above, the photosynthesis process combined with unique systems inside helps coconut trees transform the water from the ground into nutritious water.
- Myth 3 – Coconut water is diuretic
Before debunking this myth, you should know what diuretic means. Diuretics, or water medicines, contain substances that stimulate the process of moving extra fluid and salt out of your body. According to some studies, coconut water might have a mild anti-diuretic effect. However, scientific evidence is not enough to support both claims.
Besides debunking common myths about coconut water and its formation, you can learn how magical the natural process works inside the tree to produce healthy and delicious water.
Benefits of coconut water

Coconut water is a famously healthy drink, but how is it good for our health? We will go through some main coconut water benefits when adding this drink to your diet.
- Hydration and electrolyte replenishment
Human bodies need a great amount of water for effective functions. A natural source of electrolytes, such as potassium, sodium, and magnesium, inside coconut water helps balance fluid and keep our bodies continuously hydrated.
Besides hydration, the minerals inside coconut water can replenish lost electrolytes after intense physical activities or severe illnesses. Thus, it can save you from muscle cramps and fatigue.
- Potential health benefits

It may be a surprise, but drinking coconut water is great for your heart health thanks to its potassium content. This substance can counteract the effects of sodium. Hence blood pressure becomes lower in your heart.
Another advantage of coconut water is that it can stimulate your digestion functions. Some studies also suggest that it can ease digestive issues such as constipation.
“How do coconuts get water in them?” the relevant illumination above reveals the nutrient content inside coconut water. These substances inside coconut water can increase urine volume while saving you from accumulating stone-forming factors. Hence, coconut water may help prevent kidney stone formation and protect your health.
- A natural alternative
The good news for those who follow a diet or want to lose weight is that coconut water is a low-calorie beverage. It means you can drink coconut to alter sugary drinks without sacrificing your sweet tastes while keeping track of your weight management.
You may also want to find out why young coconuts contain more water than mature ones and compare the amount of minerals in different stages.
Conclusion
The article hopefully brings out interesting facts about coconut water, a common tropical drink. The curiosity about “how do coconuts get water in them?” leads us to decode the natural processes in which coconut gets water and collects healthy nutrients.
Besides, you can also learn how beneficial coconut water is for your health while clarifying some common myths about this drink. If you want wholesale coconut water and coconut-made-from product suppliers, check out SourceVietnam.com for your reference.
FAQs
How do coconuts get their water?
The process in which water gets into coconuts involves complex systems, yet we can break it down into some primary steps, including root absorption, xylem transport, endosperm formation, and maturation. Hence, coconut palm trees transform water from the ground and add essential nutrients.
Why do young coconuts have more water?
Simply because young coconuts are in the early stages of development, when the liquid inside the coconut focuses on creating embryos, in the following stages, the liquid will gradually transform into solid white flesh instead of embryo development. The coconut water will consequently decrease.
Is coconut water similar to coconut milk?
No, it is not. Despite coming from the same fruit, coconut water contains different products with distinct properties. Specifically, coconut water is the liquid inside a coconut, while coconut milk extracts creamy liquid from the grated flesh of mature coconuts.
What are the benefits of adding coconut water to your diet?
Learning to answer “How do coconuts get water?” can illuminate what your health benefits from coconut water.
- Keep your body hydrated and also replenish lost electrolytes after doing exercise or attending intense sports activities, thanks to the natural electrolytes inside coconut water.
- Aid in your heart and kidney health by lowering blood pressure and decreasing stone-forming substances.