The ability to understand “how to calculate total manufacturing cost” in manufacturing is key to optimizing revenues and still remaining competitive in the market. Cost management is paramount in the manufacturing segment which small fluctuations can significantly impact the bottom line.

Total manufacturing cost is an important metric for understanding a business’s overall expenses and profitability. This blog post will provide a comprehensive guide, providing a clear and step-by-step approach to calculating and interpreting total manufacturing costs effectively.
What is the total manufacturing cost?
Total manufacturing cost (TMC) also means total manufacturing cost, which is the total cost of all the activities to convert all the raw materials into a completed product. It is crucial in the business and reveals a certain order of the production processes in relation to the set objectives.

TMC consists of three elements, which are as follows:
Direct materials
As the name indicates, these are the most recognizable elements that constitute the finished goods. Direct materials are the core components used in manufacturing finished goods. Examples include fabric for clothing, steel for automobiles, and wood for furniture. These materials are easily identifiable within the final product.
Direct labour
This is the main component of the word but, more specifically, defines the amount of money paid to workers who process the raw materials into finished goods. Such as workers could be assembly machine operators, line workers, and even quality control inspectors.
Manufacturing overhead
This category covers all expenses which are needed to implement the production processes but cannot be physically identified with a specific unit of output. Manufacturing overhead expenses include amounts paid for renting premises and utilities, depreciation on machines, machinery, and property insurance, payment of supervisory and managerial staff, and expenses on indirect materials like oils and detergents.
Read more >>> What Is Contract Manufacturing? A Complete Guide for 2025
Calculating total manufacturing cost
Formula on how to calculate total manufacturing cost
Total manufacturing costs contain three key business costs: direct labour, direct material, and manufacturing overhead costs. To calculate your total manufacturing cost, you can leverage the following manufacturing calculation:
Total manufacturing cost formula = Direct materials + Direct labour + Manufacturing overhead
What are direct materials?
Direct materials are the integral components of product manufacturing. They are all raw materials directly used in production, which is easily traced back to it.
Direct materials = Tally material purchased for the last period + Cost of opening inventory – The cost of ending inventory
For example, each T-shirt requires 2 yards of fabric priced at 5$. It means the total cost of fabric is 10$. If the thread used costs about 1$ and the label is approximately 0.5$. So the total direct material will be 11.5$.

What is direct labour?
Direct labour constitutes all labour that is involved directly in the physical process of production, i.e., the labour needed to convert raw materials into a sellable good, not including management, maintenance, accounting staff, etc.
Hourly labour rate = (Total wages + taxes + other benefits costs) / Total number of labour working hours
Or
Direct labour cost per unit = Direct hour labour rate x Direct labour hours
For example, the wages paid to employees who are directly involved in production, such as processing teams, workers on the assembly line, machine operators, supervisors, QA inspectors, and even staff in warehousing and delivery. Delivery services are also included in operational efficiency

What is manufacturing overhead?
Manufacturing overhead costs are also known as indirect manufacturing costs. These expenses are necessary for the production process to possibly occur like:
- Mortgage or facility rent
- Facility insurance and utilities like water, electricity, taxes, etc.
- Maintenance and repair fee
- Facility and equipment depreciation
- Staff labour for QA, cleaning, supervisor, product management, etc.
Step-by-step guide to calculating manufacturing overhead calculation:
Manufacturing overhead = Overhead costs / Sales x 100
Read more >>> What Does MOQ Mean in Manufacturing?
What are fixed costs?
Fixed costs don’t fluctuate with changes in production volume. These expenses don’t relate to business operational efficiency activities. Understanding fixed costs in manufacturing and having a knowledge of calculate fixed costs is essential for accurate cost accounting and financial analysis.
Here are some common examples of fixed costs in manufacturing:
- Rent and property taxes for the factory building and storage facilities
- Insurance for property, liability, and compensation for workers
- Salaries of administrative staff, managers, and supervisors (excluding production floor workers)
- Depreciation of manufacturing equipment and machinery
Fixed cost = Total production cost – (Variable costs per unit x Number of units produced)

Calculate your manufacturing cost per unit for better pricing
After the fixed costs are explained, but still wondering how to calculate cost per unit? Here’s the formula for calculating manufacturing cost per unit (MCU)
MCU = Total manufacturing cost / Number of units produced
This fee is a metric that reflects the average cost of producing a single unit. Businesses can set optimal selling prices and analyze the profitability.
Example:
For instance, a firm produces 10,000 units of wooden tables in a month, and the entire table-making process in that month costs around $500,000. The unit cost which can be deducted from the above estimation may be calculated as follows:
MCU = $500,000 / 10,000 units = $50 per units
This indicates that the average cost to produce each table is $50. This data is helpful in setting the lowest purchase price that will guarantee a profit after recovering such items as advertising, distributing, and administration expenses.
Direct vs indirect costs: a comparison in relation to the manufacturing
Proper accounting records can enhance the effectiveness of any business. Knowing the direct and indirect costs is essential for pricing and for other crucial financing decisions that a company undertakes. And knowing the difference between direct and indirect manufacturing costs assists you in resource allocation for maximizing the profit potential of an entity.
- Direct costs: They are related to a particular output and can be directly associated with that output. These costs can also be easily traced back and accounted for with respect to every product. Examples include the finished goods’ direct material components and direct labour costs that, at a minimum, can be sourced in the production of the item.
- Indirect costs: These costs are defined as costs incurred in relation to the entire class of products, but not a specific item. They can be allocated but should not be interpreted as being able to be replaced by resources with respect to a class of production. For example: rent, utilities, and supervisors’ salaries are all included.

Importance of total manufacturing cost in pricing strategy
Accurately determining the total manufacturing cost is foundational for successful pricing strategies.
Pricing decisions
With an understanding of this cost, businesses can set prices that are not only able to recoup the cost but also leave a reasonable profit margin calculation on the product. If a business is unable to define its manufacturing costs properly, it will tend to sell its products at discounted prices with potential losses or sell them above the price that can be competitive.
Profitability analysis
Profitability analysis is significantly impacted by an understanding of how to calculate total manufacturing cost. By breaking down these costs, businesses can pinpoint areas for improvement and cost reduction. This analysis enables informed decisions about pricing, production volume, and cost control in manufacturing.
Profit margin analysis
Revenue that remains after the cost of goods sold (COGS) is removed can be expressed as a percentage of sales. COGS is composed of direct materials and direct labour, but it does not normally include manufacturing overheads.
Understanding a gross margin allows businesses to recognize strengths in their cost structure and assist in decisions regarding sales prices, volume of production and mix of products.
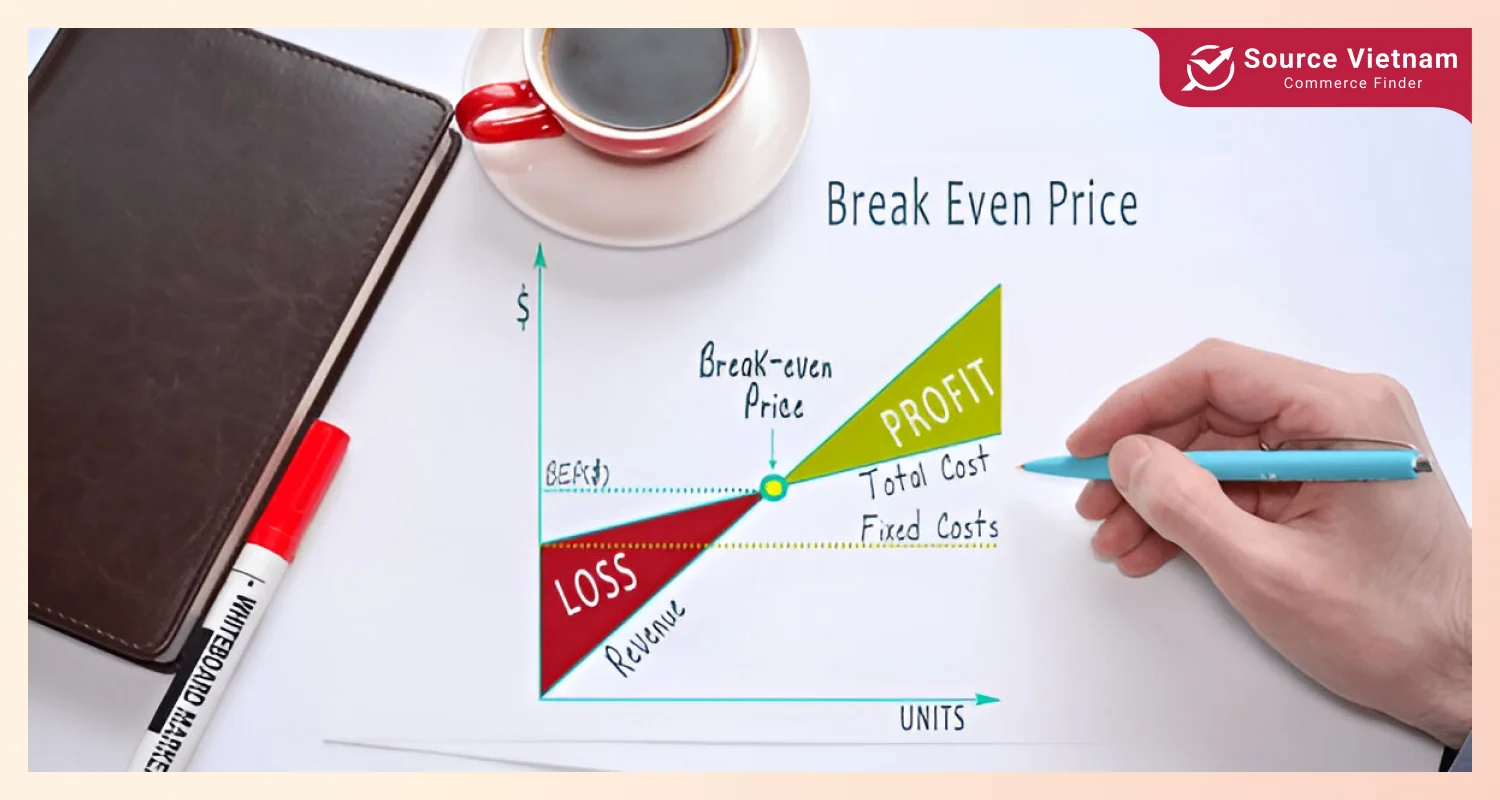
Break-even analysis
The break-even point is relevant to a business, so it can account for the amount of goods or services. This needs to be produced and sold to generate sufficient income to cover all costs, both fixed and variable. A break-even point allows you to foresee the level of production volume, set the price, and even decide whether to buy new machines or tools, as one is able to know ahead of time how much will be spent.
Conclusion
In conclusion, accurately calculating and interpreting total manufacturing cost is a cornerstone of successful manufacturing operations. Gaining knowledge on how to calculate total manufacturing cost will assist a business to make reasonable business decisions regarding pricing policies, output level and cost control measures.
Thus, organizations are able to justify the more efficient production operations and, subsequently, improve the competitiveness as well as the profitability. To gain a deeper understanding of manufacturing cost calculations and their impact on your business, visit SourceVietnam.com today.
FAQs
What are the different types of manufacturing costs?
Three categories encompassing manufacturing costs are as follows:
- Direct materials – these are the products that go through the physical change of being transformed and worked on during the production processes.
- Direct labour – these are the items costs that comprised the payment of wages to the workers that were working directly in an area engaged in manufacturing.
- Manufacturing overhead – these are costs that were not directly tied to the production process, such as rent, utilities, maintenance, etc.
What are the key components of total manufacturing cost?
Total manufacturing cost is the sum of all expenses incurred in the production process. Key components include:
- Direct materials cost
- Direct labour cost
- Manufacturing overhead cost
What is the method for overhead cost calculation?
Total manufacturing cost is the accumulation of every charge that arises due to the cost incurred in manufacturing all the products. A production cost numerator is found by a total that expresses the production cost incurred by the manufacturing firm.
How do I cut down manufacturing costs?
To reduce manufacturing costs, consider:
- Negotiating better prices with suppliers
- Improving production manufacturing efficiency
- Implementing lean manufacturing principles
- Investing in automation
- Outsourcing non-core function
How is pricing affected by the different types of manufacturing costs?
It’s vital to understand manufacturing expenses as it will facilitate the determination of profitable prices. If a company is able to accurately calculate the cost of production, they can:
- Avoid underpricing products and incurring losses
- Choose competitive prices that cover revenues and expenses
- Identify areas for cost promotion to improve margins